Enzyme inhibitors prevent the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex and hence prevent the formation of product. Inhibition of enzymes may be either reversible or irreversible depending on the specific effect of the inhibitor being used.
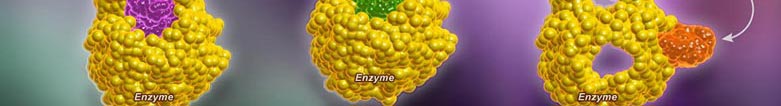
In a normal reaction, a substrate binds to an enzyme (via the active site) to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The shape and properties of the substrate and active site are complementary, resulting in enzyme-substrate specificity. When binding occurs, the active site undergoes a conformational change to optimally interact with the substrate. This conformational change destabilizes chemical bonds within the substrate, lowering the activation energy. As a consequence ofthis enzyme interaction, the substrate is converted into product at an accelerated rate.
A competitive inhibition involves a molecule, other than the substrate, binding to the enzyme’s active site. The molecule (inhibitor) is structurally and chemically similar to the substrate (hence able to bind to the active site). The competitive inhibitor blocks the active site and thus prevents substrate binding. As the inhibitor is in competition with the substrate, its effects can be reduced by increasing substrate concentration.
A non-competitive inhibition involves a molecule binding to a site other than the active site (an allosteric site). The binding of the inhibitor to the allosteric site causes a conformational change to the enzyme’s active site. As a result of this change, the active site and substrate no longer share specificity, meaning the substrate cannot bind. As the inhibitor is not in direct competition with the substrate, increasing substrate levels cannot mitigate the inhibitor’s effect.
Drugs that function as enzyme inhibitors constitute a significant portion of the orally bioavailable therapeutic agents that are in clinical use today. Most of the drug discovery and development efforts at present are focused on identifying and optimizing drug candidates that act through inhibition of specific enzyme targets. The attractiveness of enzymes as targets for drug discovery stems from the high levels of disease association (target validation) and druggability (target tractability) that typically characterize this class of proteins.
Aurora Medbiochem is proud to offer a variety of structurally diverse enzyme inhibitors for research.
A specific, irreversible serine protease inhibitor. Inhibits proteases like chymotrypsin, kallikrein, plasmin, thrombin and trypsin. A stable, non-toxic and better soluble alternative to PMSF.
Bestatin is a protease Inhibitor that reversibly inhibits amino peptidases.
Bortezomib is a cell-permeable dipeptidylboronate compound that acts as a potent and selective 26S proteasome inhibitor. Human pancreatic cancer cell studies demonstrate Bortezomib to inhibit the PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase and enhance ER stress, leading to apoptosis.
MG-132 is a cell-permeable, potent, and reversible proteasome inhibitor (Ki = 4 nM). Reduces degradation of ubiquitin-conjugated proteins in mammalian cells and permeable strains of yeast by the 26S complex without affecting its ATPase or isopeptidase activities. Activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1), which initiates apoptosis. Inhibits NF-kB activation (IC₅₀ = 3 µM). Prevents γ-secretase cleavage.
A 10 mM (5 mg in 1051 µl) solution of MG-132 (Cat. No. AUR10625) in anhydrous DMSO.
NDSB-221 is a nondetergent sulfobetaine that has been found to improve unfolding reversibility. Increases the extraction yield of membrane, nuclear and cytoskeletal associated proteins.
A cocktail of six broad specificity protease inhibitors that can provide maximal protection to prevent degradation of proteins in mammalian tissue extracts as well as both mammalian and bacterial cell extracts by inhibition of various serine, cysteine, aspartic proteases and aminopeptidases. This cocktail is EDTA-free making it broadly applicable for any downstream application that is affected by the presence of metal chelators.
A cocktail of four protease inhibitors that have been optimized for the inhibition of serine and cysteine but not metalloproteases. Since this cocktail does not contain any EDTA, metal-dependent proteins and IMAC (immobilized metal affinity chromatography) isolation techniques (e.g. for poly-His-tagged proteins) are not affected. Reconstitute each vial with 1 ml D.I water to obtain a 100X concentrated stock solution.
A cocktail of six broad specificity protease inhibitors (see table above) that can provide maximal protection to prevent degradation of proteins in mammalian tissue extracts as well as both mammalian and bacterial cell extracts by inhibition of various serine, cysteine, aspartic proteases and aminopeptidases.